One of my favorite things in SQL Server is Filtered index . Filtered index helps us in higher selectivity and also in decreased storage consumption , if the query criteria looks only for pre defined. sub set of data .
Let us say , you got a table of 50 million records , out of which only 50,000 are active records and your application only looks for active records . Then filtered index will make much more sense .
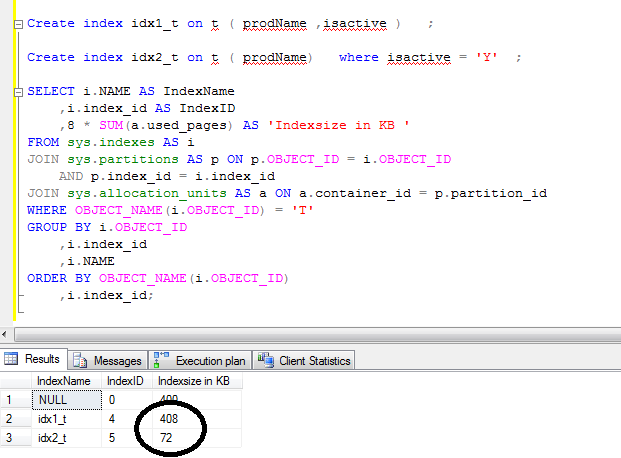
Here is an example.


As you can see , there is a significant difference in the index size.
The query optimizer uses the second indexes , whenever , there is query looks for any ACTIVE product.
In Oracle , we can simulate the filtered index with Function Based Index .
SQL> drop table t purge ;
Table dropped.
SQL> Create table t as select * from all_objects ;
Table created.
SQL> Create index idx1_t on t( owner , object_type ) ;
Index created.
SQL> exec dbms_stats.gather_table_stats(user , 'T') ;
PL/SQL procedure successfully completed.
SQL> analyze index idx1_t validate structure ;
Index analyzed.
SQL> col name format a15
SQL> Select name , height , blocks , lf_rows , lf_blks , btree_space , used_space from index_stats ;
NAME HEIGHT BLOCKS LF_ROWS LF_BLKS BTREE_SPACE USED_SPACE
--------------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ----------- ----------
IDX1_T 3 384 93172 336 2712096 2415824
Now , let us create a FBI , where I am interested only in 'MATERIALIZED VIEW' of a user.
SQL> Create index idx2_t on t( owner , case when object_type = 'MATERIALIZED VIEW' then 'MATERIALIZED VIEW' end ) ;
Index created.
SQL> analyze index idx2_t validate structure ;
Index analyzed.
SQL> Select name , height , blocks , lf_rows , lf_blks , btree_space , used_space from index_stats ;
NAME HEIGHT BLOCKS LF_ROWS LF_BLKS BTREE_SPACE USED_SPACE
--------------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ----------- ----------
IDX2_T 2 256 93172 232 1864032 1664870
As you can see, the storage has decreased from 2712096 to 1864032 , leaf blocks from 336 to 232 and also like the height of the index from 3 to 2 , which helps the optimizer to relatively find the data faster.
Comments welcome.

No comments:
Post a Comment